What is Income as per Income Tax Act?
The word Income has a very broad and inclusive meaning which is defined under section 2(24) of income tax act, without getting too in depth we will understand it broadly.
- In case of a salaried person, whatever amount received from an employer, either in cash or kind or as a facility is considered as income.
- For a businessman, his profits and gains will constitute income
- For professionals, freelancers etc. there earnings from various sources like professional fees, other incomes etc. are considered as Income.
- You might receive Rental income from house owned.
- Or capital gains from sale of shares, buying or selling of property etc.
- Income may also flow from investments in the form of Interest, Dividend, and Commission etc.
- Income Tax Department has classified income in 5 broad categories. Those are:
- Income from Salary : The amount received by you from your employer every month comes under the head
income from salary. As per law, employer-employee relationship is must to consider the amount as income from salary else it will be considered under other head and therefore exemptions, allowances available to a salaried individuals will not be available.
The amount of your Salary includes basic pay, dearness allowance, medical, transport, annuity, gratuity, advance of salary, allowances, commission, perquisites in lieu of salary and retirement benefits etc.; The aggregate of the above incomes, after the exemptions but before the deductions, is known as Gross Salary and this is charged under the head income from salary. (you can refer to column no. 6 of your Form- 16 to know your taxable salary amount) - Income from House property : Any Rental Income from residential or commercial property that you own will be taxed. If you have home loan then interest part of it would also be considered as negative income from House property.
- Income from Business or Profession : Income earned through business or profession is taxable under the head ‘profits and gains of business or profession. The income on which tax is levied shall be net of expenses.
- The income on which tax is levied shall be net of expenses.
- Income from capital gains : Any profit or gain arising from transfer of capital asset held as investments (such as house, Jewellery are chargeable to tax under the head capital gains. The gain can be on account of short-term and long-term gains. Our article Basics of Capital Gain talks about it in detail.
- Income from other sources : Any income that does not come under the above four heads of income is taxed under the head income from other sources. For eg. savings bank interest,lottery you win (probably never :P) or Reality shows like “Kaun Banega crorepati” etc. all these Incomes are taxable that means the person winning 1 Crore in the show will have to pay 30% of tax. so he actually never became crorepati ;)
- Income from Salary : The amount received by you from your employer every month comes under the head
income from salary. As per law, employer-employee relationship is must to consider the amount as income from salary else it will be considered under other head and therefore exemptions, allowances available to a salaried individuals will not be available.
Refer to the table below to get an idea about the various classifications of income:

While your hard earned income is generally taxable, there are certain categories of income that are exempted, these are called tax free incomes and are provided in Section 10 of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Tax Free Incomes – The Essential List Part-I
What are Exempt Incomes/Tax Free Income and Taxable Incomes?
Exempt Incomes are not chargeable to tax as per Income Tax law i.e. they are not included in the total income for the purpose of tax calculation. Eg Interest earned from PPF etc. While, taxable Incomes are chargeable to tax eg. Salary, House Property, Capital Gains Income Etc.
What is PAN?
PAN stands for Permanent Account Number, it’s a ten-digit unique alphanumeric number issued by the Income Tax Department that acts as an identification for us. Whether we are Individual, HUF, Company, Firm, or any other assessee, the same can be known through our PAN . PAN is a prerequisite for filing ITR, also the tax department can trace all our communications, returns, refunds, and other activities relating to Income Tax through our PAN. It looks like as shown in image.
Where,
First Five digits will always be Alphabetic, Next four digits - Numeric and the Last digit - Alphabetic
But, the 4th letter is important as it denotes type of assessee (Individual ,Company, Firm Etc.)

Given below is an illustrative PAN: AAAAA1234A
Every person having a PAN needs to file ITR?
No, only those having taxable income or otherwise come under the ambit of mandatory filing of Income Tax return as per Income Tax Act are required to file ITR.
What is TAN?
TAN refers to Tax Deduction Number which is a 10 digit alphanumeric number allotted to those who are liable to deduct TDS by the Income Tax Department.
TAN Format- JPRD00214F
First Four digit Alphabetic, than after Five digit Numeric and last digit is Alphabetic.
Who is an assessee?
As per Income Tax Act, an assessee means “a person by whom any tax or any other sum of money is payable under this Act”.
In layman’s term if you are liable to pay taxes, have any taxable income, or otherwise required to file ITR, you are an assessee. The Income Tax Act, 1961 has classified Assessee in different categories, such as
| Individual | Piyush Aakash |
| Partnership Firm | M/s ABC and Company M/s ABC and associates |
| A Hindu Undivided Family | Mr. A (HUF) or Mr. B (HUF) |
| Company | Winiin Taxscope Private Ltd. Winiin Taxscope Ltd. |
| An AOP (Association Of Persons) or BOI (Body Of Individuals) | ABC Sangh XYZ Dal |
| A Local Authority | Pune Municipal Corporation PCMC Municipal Corporation |
| Artificial Juridical Persons | Everyone not falling within any of the above categories. |
What is the difference between Financial Year and Assessment Year?
Financial Year is the year in which you have earned income On the other hand, Assessment Year is always the succeeding year in which you file your Previous Year Income Tax Return, and offer the particulars of your income earned during the Previous Year to be assessed by the Income Tax Department.
What is Income Tax?
An income tax is a tax imposed by government on income earned by you. Income tax is a key source of funds that the government uses to fund its activities and serve the public.
What is Corporate Tax?
When Companies pay taxes under the Income Tax Act it is normally called Corporate tax.
Which body governs filing of taxes in India?
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) provides essential inputs for policy and planning of direct taxes in India and is also responsible for administration of the direct tax laws through Income Tax Department.
CPC Bengaluru or Income Tax Centralized Processing Centre undertakes the work of receiving and processing all income tax returns filed in India.
Do I have to file my Income Tax Return?
Whether you are required to file your income tax return or not depends upon a number of conditions. One such basic condition being, if your income exceeds Rs. 2,50,000 in a Financial Year you are required to file ITR. For more details read our blog https://filemytaxonline.comis-it-mandatory-to-file-income-tax-return/
What documents are required to be gathered to e-file your income tax returns in India?
Go through this list to see the documents you’ll need to do your taxes. You won’t need all the documents listed here as they vary on a case-to-case basis :-
| SOURCES OF INCOME | REQUIREMENTS |
|---|---|
| **Mandatory | PAN Card |
| Bank Account Details | |
Salary |
Form 16, 16A, 26AS |
| Pay slips | |
| Rent receipt for HRA | |
| Investment under section 80C, 80D, 80E, 80G | |
House Property |
Address of property |
| Home loan interest certificate | |
| Co-owner’s details including their PAN card details & share in capital | |
Capital Gains |
ELSS, SIPs, debt funds, mutual fund statement, purchase and sale of equity funds. |
| If there is capital gains through selling shares then stock trading statement is needed | |
| purchase price, selling price, capital gain details and details of registration, in case a house property is sold | |
Other Sources |
Income received from post office account |
| Bank details required if Interest is received from savings account | |
| Reporting of interest received from corporate bonds and tax saving bonds |
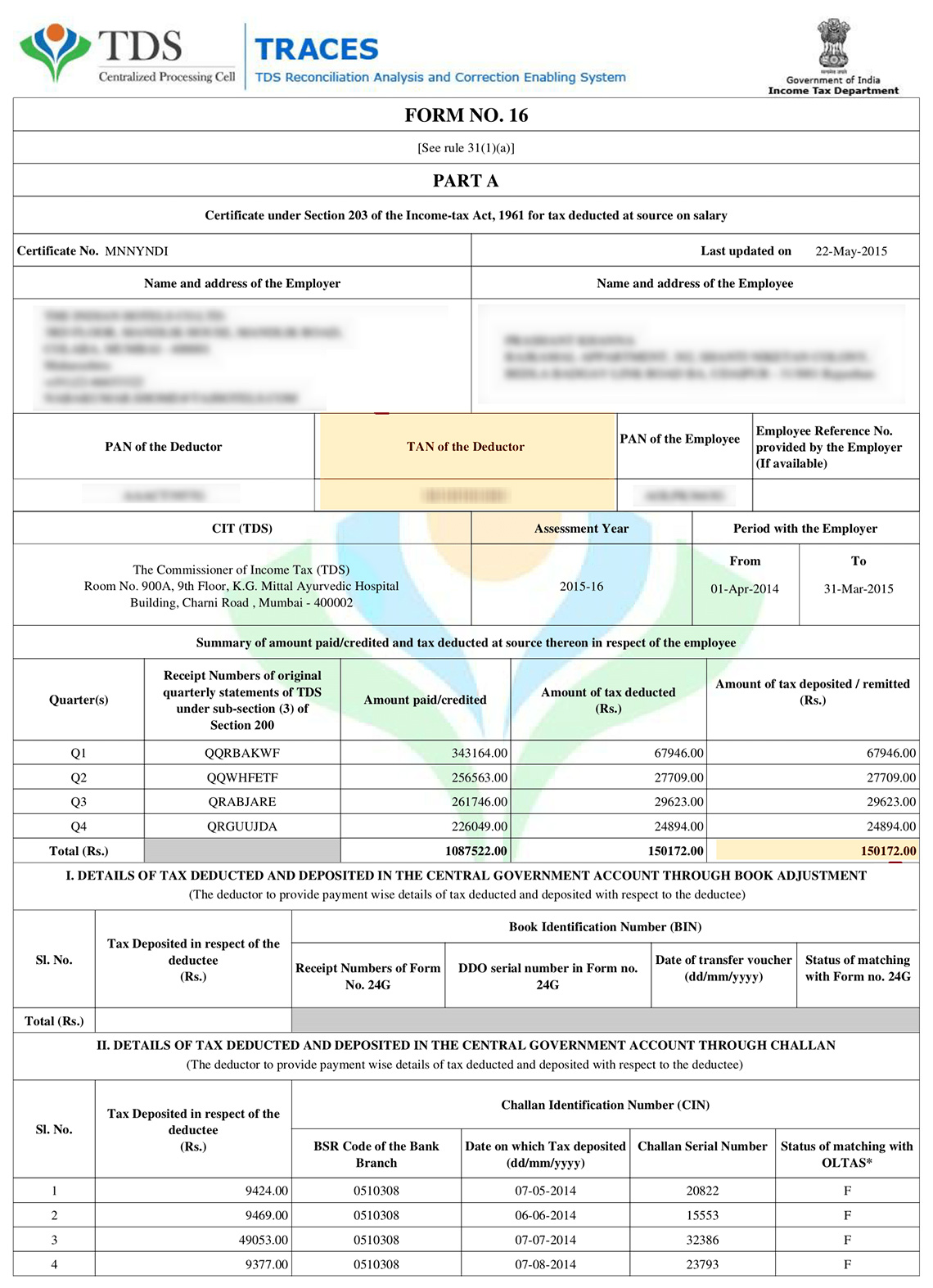
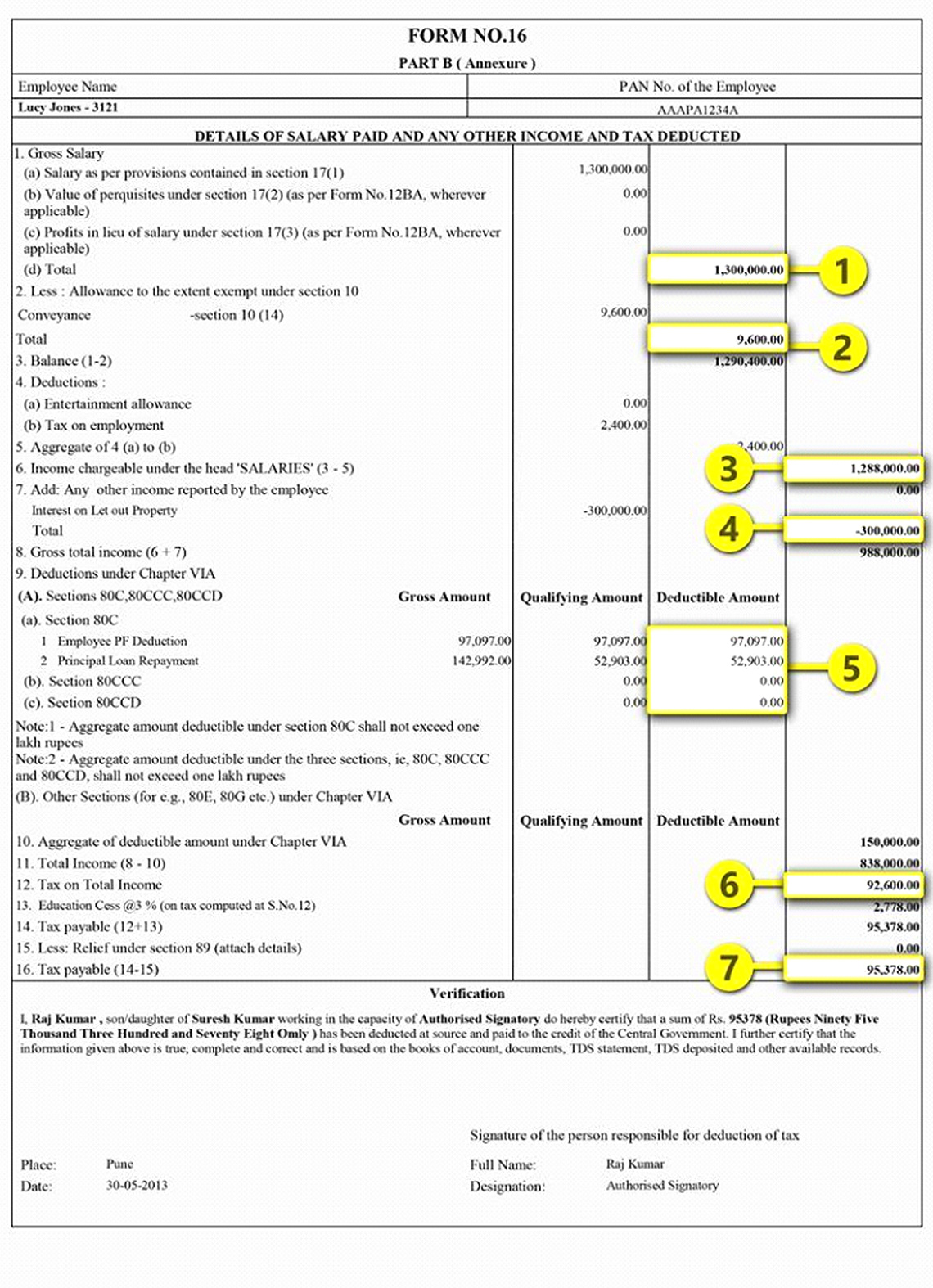
What is Form-16?
Form 16 is issued to salaried individuals, by their employers.This form prescribes details regarding
- TDS deducted and
- The Salary and Amount Received
- Allowances (like amount paid for HRA, medical reimbursements etc)
- Other Income if detail provided to the Employer.
- Deductions etc
Form is given at the end of year and helps you file your income tax return as a breeze .
It is to be noted that deduction of TDS does not free you from the mandate of Filing of Income tax return.
Form 16 might differ in formats depending upon employer to employer but a standard form 16 looks like this :-
Form 16 might differ in formats depending upon employer to employer but a standard form 16 looks like this :-
- Part A of FORM 16 contains details of tax which has already been paid by you or deducted from your income
- Part B gives the detailed breakup / composition of your income
What is TDS?
As per Income Tax Act, there are certain payments including salary, interest etc. in which the one who makes such payment is liable to deduct tax known as Tax Deducted at Source. At the end TDS is adjusted with taxes payable at the time of making final computation of income.
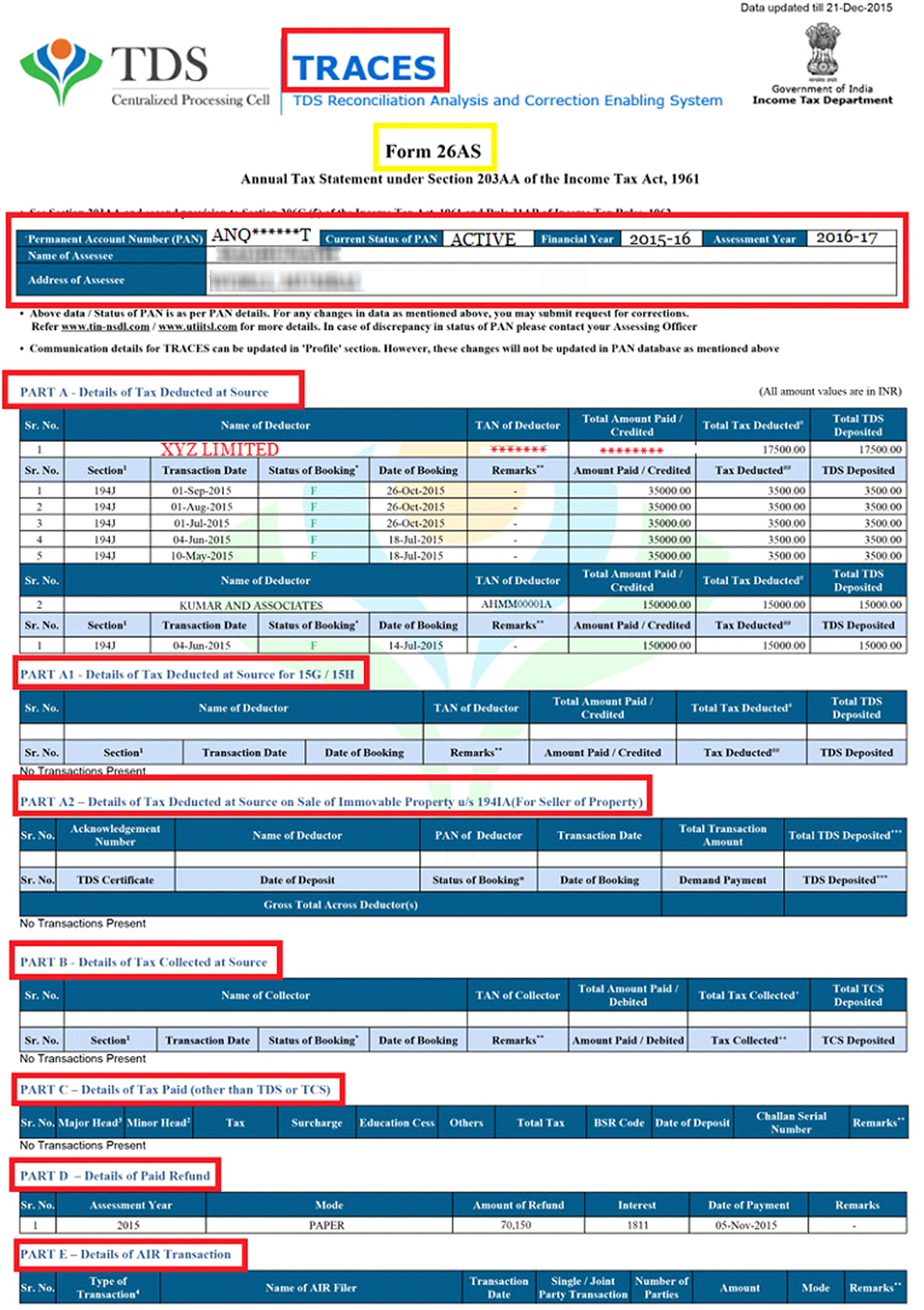
What is Form 26AS?
Form 26AS is a statement maintained and generated by the Income Tax Department for each individual assessee (person). Form 26AS is also known as annual statement which contains all tax related information of a taxpayer. The details give a clearer picture of the tax commitments of a taxpayer. It is associated with PAN. Form 26AS contains:
- Details of tax deducted on your income by deductors
- Details of tax collected by collectors
- Advance tax paid by the taxpayer
- Self-assessment tax payments
- Regular assessment tax deposited by the taxpayers (PAN holders)
- Refund received during the financial year
- High value Transactions in respect of shares, mutual fund etc. performed during the year
Link: https://incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in/e-Filing/UserLogin/LoginHome.html?nextPage=taxCred
Specimen of form 26 AS:
What is the User ID to login on Income Tax India efiling website?
The user ID is your PAN number.
What are Income Tax Forms?
These are prescribed forms through which a person can furnish the details of his /her income earned and taxes paid for the relevant financial year to the Income Tax Department. The ITR forms on successful submission to the tax department becomes Income Tax Return.
Can I file my return even if I don’t have my Form-16?
Yes, you can file your return without Form-16. You’ll just have to enter your total salary received / taxable salary and TDS deducted on it with the help of your payslips and you’re good to go.
Can Paper Return be Filed?
Yes, as per new ITR Forms and instructions issued by CBDT for Financial Year 2017-18 return in paper form can be submitted if,
- Your total income does not exceed Rs 5 lakhs But, no claim for refund could be admitted through paper filed ITRs or
- You are aged 80 years and above
Are there any benefits of filing ITR online?
In comparison to offline filing, filing your income tax return online is much faster, secure and simpler. Moreover, it is now mandatory to file your income tax return online if your income exceeds Rs. 5,00,000 in a financial year or if you want to claim the refund. You can easily e file your ITR by just uploading Form 16 at File My Tax online!!
What is ITR Form ? How ITR submitted to Department?
ITR forms as already discussed are the prescribed forms in which information is needed to be furnished to the income tax department. There are different ITR forms for different categories of assessee and the same have been explained below :-
Form and their Description
| ITR- 1(SAHAJ) | Resident Individuals having income from
|
| ITR-2 | Individuals and HUFs not having income from Profits and Gains of Business or Profession |
| ITR- 3 | Individuals and HUFs earning income from Business or Profession, including partnership firms |
| ITR-4 (SUGAM) | Anyone offering income for presumptive taxation |
| ITR-5 | Every person other than
|
| ITR-6 | For companies other than companies claiming exemption u/s 11 |
| ITR-7 | For persons including companies required to furnish return u/s 139(4A) or 139(4B) or 139(4C) or 139(4D) or 139(4E) or 139(4F). |
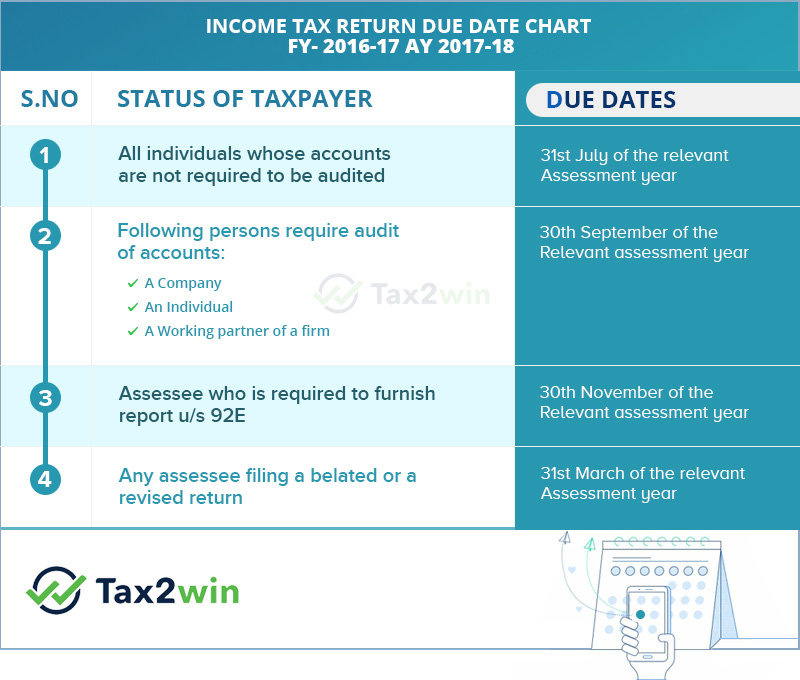
On which date ITR needs to be filed?
In simple words and for practical purpose these two due dates are relevant
- For individual - 31st July every assessment year [Non Audit Case]
- For Others - 30th September every assessment year [Audit Case]
But here you can take a glimpse of all other important dates as well:-
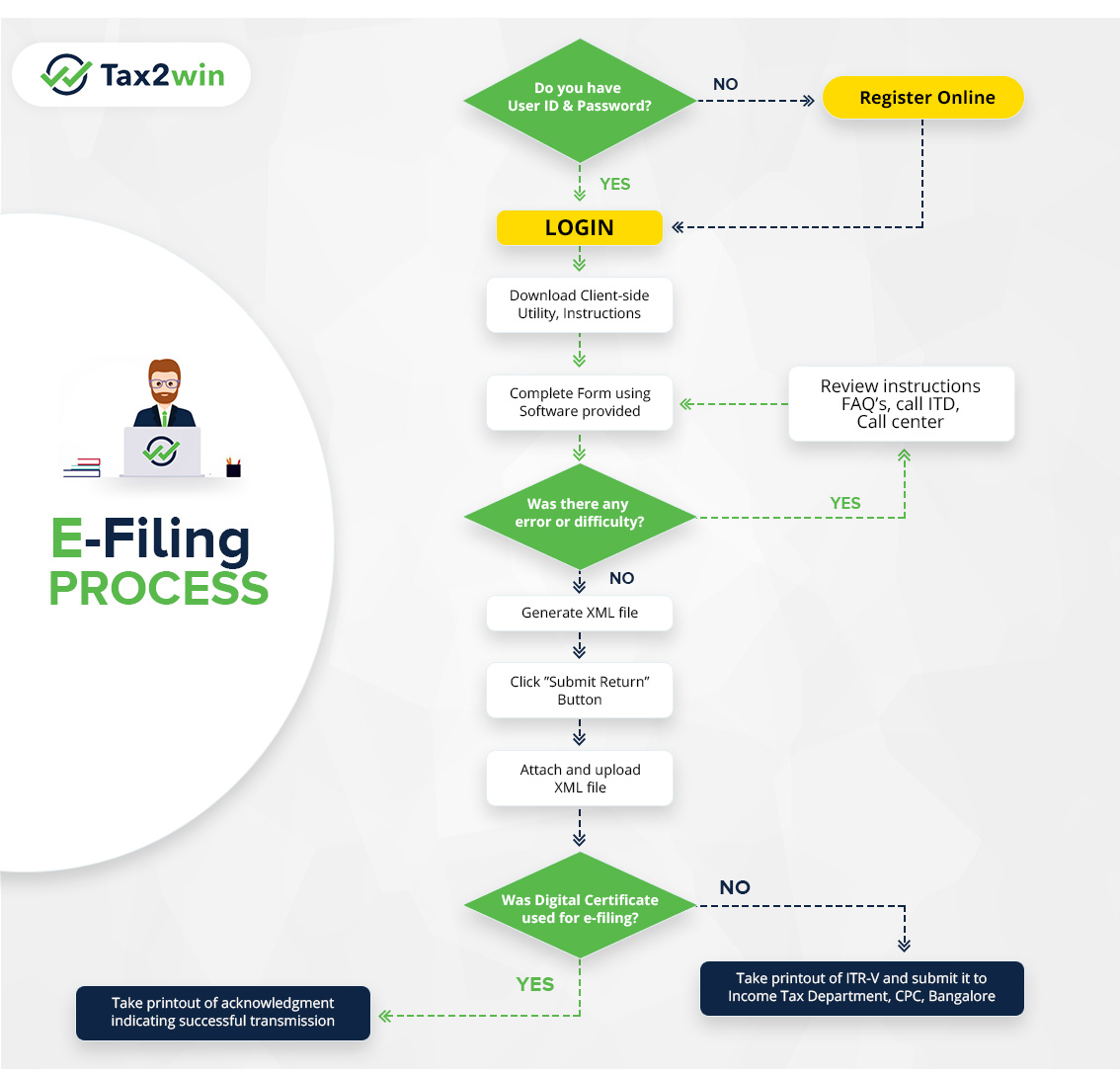
How can ITR be filed?
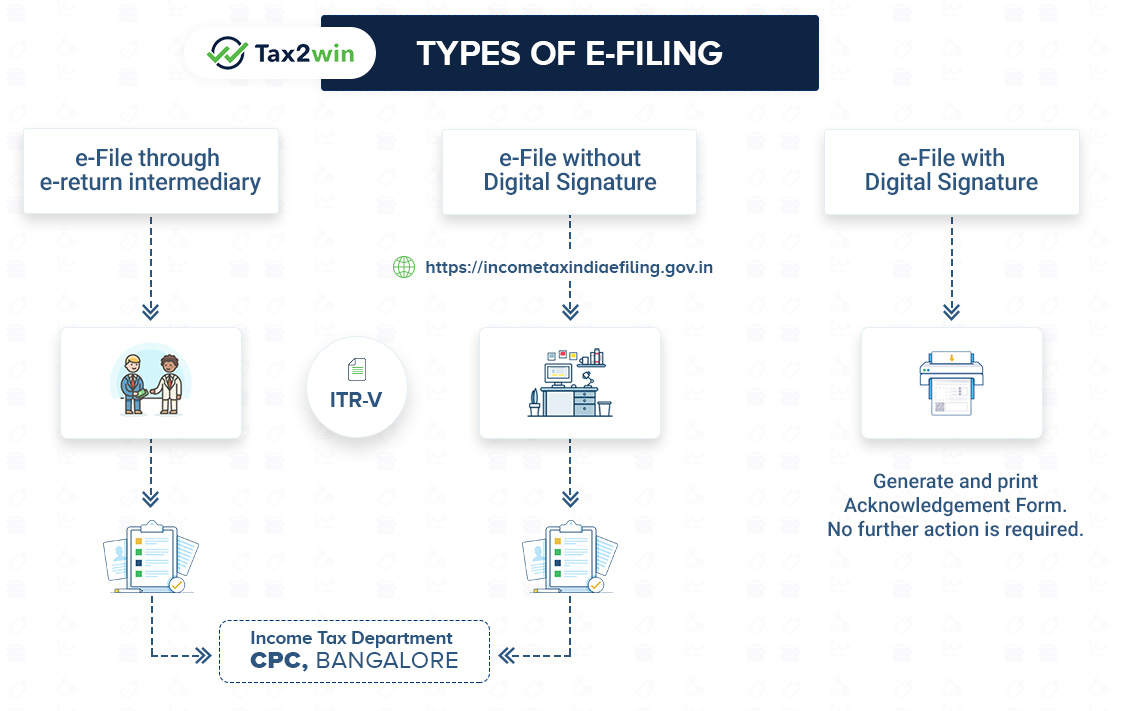
What is the process of e-filing ?
Income Tax Slab Rates for F.Y. 2019-20
There are various Income tax Slabs determined by the government depending upon the age of an individual. They are as under :
Income tax slab for Individual taxpayers & HUF (less than 60 years old)
| INCOME(Rs.) | F.Y. 2017-18 | |
| Up to Rs 2,50,000 | No Tax | |
| Rs. 2,50,001 to 5,00,000 | 5% | |
| Rs.5,00,001 to 10,00,000 | 20% | |
| Above Rs. 10,00,000 | 30% |
Income tax slab for senior citizens (60 years old or more but less than 80 years old)
| INCOME(Rs.) | F.Y. 2017-18 | |
| Up to Rs 3,00,000 | No Tax | |
| Rs. 3,00,001 to 5,00,000 | 5% | |
| Rs.5,00,001 to 10,00,000 | 20% | |
| Above Rs. 10,00,000 | 30% |
Income tax slab for super senior citizens (80 years old or more)
| INCOME(Rs.) | F.Y. 2017-18 | |
| up-to 5,00,000 | Nil | |
| Rs.5,00,001 to 10,00,000 | 20% | |
| Above Rs. 10,00,000 | 30% |
Note:-
Surcharge:
A- 15% of income tax, where total income exceeds Rs.1 crore.
B- 10% of income tax, where total income exceeds Rs.50 lakhs but up to Rs. 1 crore.
Cess:
2% on Education Cess and 1% on 3% on income tax
Rebate under Section 87A: The rebate is available to a resident individual if his total income does not exceed Rs. 3, 50,000. The amount of rebate shall be 100% of income-tax or Rs. 2,500, whichever is less.
How to calculate income tax from income tax slabs?
This example explains how to apply tax slabs to calculate income tax for FY 2017-18 (AY 2018-19).
Rohit has a total taxable income of Rs 8,00,000 i.e. income after considering the deductions under chapter VI A. Rohit wants to know his tax dues for FY 2017-18
| Income Slab | Tax Rate | Tax calculation |
| Income up to Rs 2,50,000 | No tax | |
| Income from Rs 2,50,000 – Rs 5,00,000 | 5% (Rs 5,00,000 – Rs 2,50,000) | Rs 12,500 |
| Income from Rs 5,00,000 – 10,00,000 | 20% (Rs 8,00,000 – Rs 5,00,000) | Rs 60,000 |
| Income more than Rs 10,00,000 | 30% | nil |
| Tax | Rs 72,500 | |
| Cess | 3% of Rs 72,500 | Rs 2,175 |
| Total tax in FY 2017-18 (AY 2018-19) | Rs 74,680 (Rounded off) |
What is Deduction under section 80C?
In simple terms, you can reduce up to Rs 1,50,000 from your total taxable income through section 80C, by making investment in prescribed routes like PPF, LIC etc. This deduction is allowed to an Individual or a HUF.
Example
| Income | 500000 |
| less- Deduction u/s 80C | 150000 |
| Taxable income | 350000 |
After providing deduction u/s 80C Taxable income will only be Rs 3.5 lakhs and not 5 lakhs.
What is Rebate u/s 87A?
A taxpayer who is Resident Individual having taxable income upto Rs 3.5 lakhs for the Financial Year 2017-18 and 2018-19 can get rebate for the taxes payable upto Rs 2,500. For more details and calculations read our blog on Income Tax Rebate Under Section 87A
What is Advance Tax?
Advance tax means income tax paid in advance instead of lump sum payment at the time of filing the ITR. It is also known as “Pay As You Earn” tax. These payments have to be made in instalments as per due dates provided by the Income Tax Department.
Who should pay Advance Tax?
Advance tax is to be paid by an individual if his total tax liability is Rs 10,000 or more in a Financial Year. The provision of Advance tax applies on all taxpayers. Whereas, Senior citizens, who are 60 years or older, and do not run a business, are exempt from paying advance tax.
What is Self assessment Tax?
Your income tax return cannot be submitted to the tax department, unless you have paid tax dues in full. Sometimes, you may see tax payable at the time of filing your return. This income tax must be paid online, so that return is successfully e-filed afterwards.Procedure for payment of taxes?
Taxes can be paid online by making e payment or alternatively the hard copy of the challan can be deposited in any nearest branch of a bank. For details please read click here.
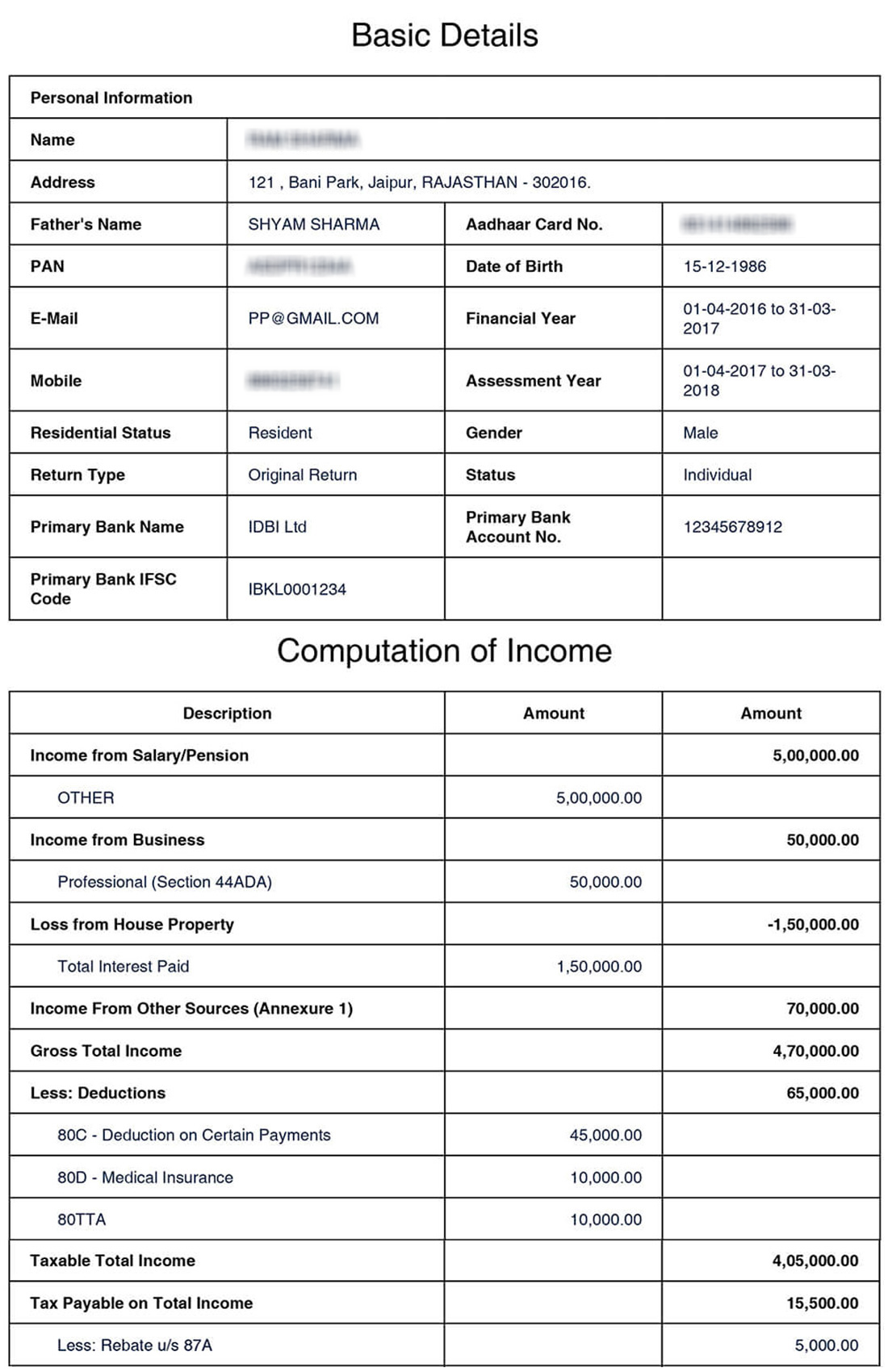
What is computation of income?
A systematic presentation of inputs entered by an assessee together with calculation of taxes is known as computation of total income. There is no fixed format for the same. Generally, following elements are considered while making Computation Of Total Income
- Personal details of assessee
- Name
- Father's name
- Address
- Contact details etc - Bank account details
- Income details and
- Calculation of taxes
- Taxes paid details
A specimen of the computation has been given here under for your reference;
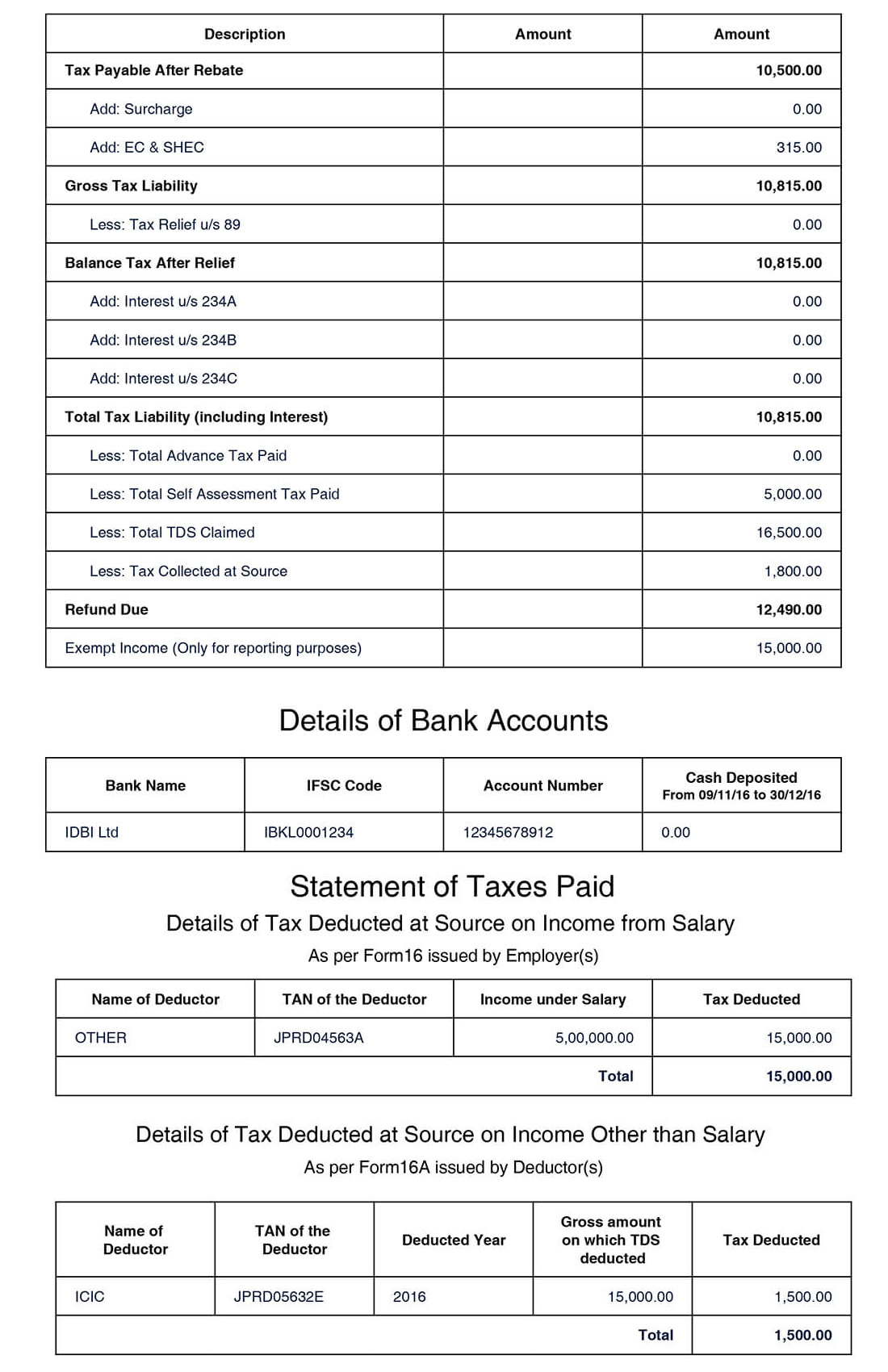
What is ITR –V?
After filing of your income tax return, the department wants to ensure via physical or electronic verification that it’s you only, who has filed the ITR and no one else misused the account. For this one pager acknowledgement/receipt is generated which is commonly termed as ITR-V. You are required to verify the same by either signing it manually and sending to CPC Bengaluru or through e verification.
A specimen of Acknowledge generated after successful filing of Income tax return has been attached herewith for your reference.
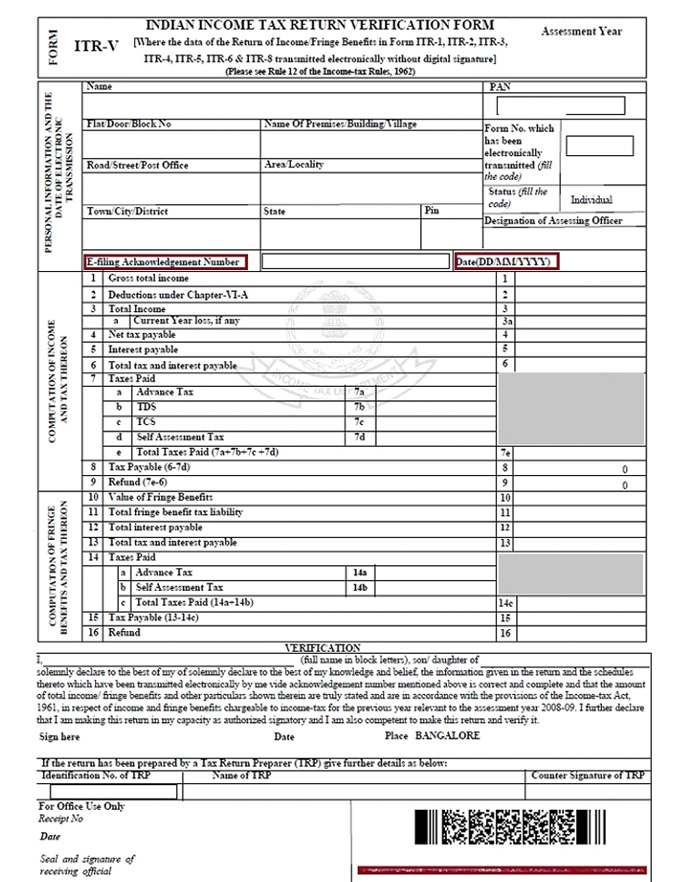
Do I need to attach any documents along with my Income Tax Return?
No, you don’t have to attach any document along with your income tax return. You are required to submit documents only when the Income Tax Department asks you to submit.
Why correct calculation of your income is important?
The tax which will be paid by you to the Income Tax Department, is calculated on your total income. Wrong computation of income may lead you in a situation of
- Paying Taxes
- Wrong selection of ITR form
- Penalty for not paying advance tax (if applicable)
- Undue cash crunch etc
Hence correct calculation of income becomes very crucial.
For example, In case of incomes earned between 1st April 2017 to 31st March 2018
| The Financial Year (FY) shall be | 2017-18 |
| And the Assessment Year (AY) will be | 2018-19 |
What if I don’t file my return?
In case you don’t file your return, following repercussions may follow:-
- A notice can be issued by the Income Tax Department.
- Any business losses during the year will not be allowed to carry forward to the next years.
- Penalty shall be imposed u/s 270A, and interest may be payable as per the section 234A,B,C
- Other consequences may also be there as per Income Tax act, 1961.
(Read our detailed blog on consequences of not filing your income tax return)
What if wrong particulars are furnished while filing Income Tax Return?
So in case you have furnished a wrong information in your income tax return, you can submit a revised return before end of the relevant assessment year in which the original income tax return was filed. I.e for Financial Year 2017-18; AY 2018-19 you can file a revised return till 31st March 2019.
Your return can now be revised irrespective of the fact, it was filed till due date or afterwards. To summarise, a belated return can also be revised.
In case of any misreporting detected in the income tax return, the income tax officer can levy a penalty of 200% of the tax which is sought to be avoided. In other cases of under reporting of income the penalty shall be restricted to 50% u/s 270A of the Income Tax Act 1961. Hence be very vigilant while disclosing your income and filing taxes.
What File My Tax online is?
File My Tax online is a Registered E-Return Intermediary by Income Tax Department, that provides a platform to bridge the gap between remote users who wish to file their Income Tax Return and tax professionals who, provide them professional assistance and prepare their Income Tax Return online. Users are no more required to visit offices of CA’s and wait for hours. Also, need to pay a significant amount as professional fee has been eliminated.
Alternatively, you can file Income Tax Return through File My Tax online’s intuitive website on their own completely free of cost.
In cases you do not want to file ITR but Seek expert tax advice you can take help of File My Tax online’s e-CA’s. Further, following free tools on the website can be of immense utility to you
- Generate Rent receipts from free tool
- Know your refund status anytime
- Apply PAN online
- Calculate your Income Tax liability
- Know the amount of HRA exemption to be claimed
- Gratuity Calculator
- TDS Calculator etc
- Know about the tax terminologies, saving tips and recent updates
Who are the users of File My Tax online website?
The users of File My Tax online are varied from Employees at all hierarchy of corporates, A Self-occupied, IT Professional, An Army Personnel, A Police Inspector, A Compounder, A Share Broker, A Doctor to A Finance Head also coving in its ambit A Businessman. Basically File My Tax online is one doorstep solution to all taxation needs of every kind of a user.
In what form information is transmitted by File My Tax online to the Income Tax Department?
What we see on website is front end but information with tax department is filed in ITR forms as referred above namely, ITR 1,2 etc) and based on these ITR forms we develop back end of our software.
Will it make any difference in Income tax if an assessee is a resident or non resident?
Yes, it makes a big difference under Income tax provisions as there are different tax provisions for them. Hence, due care has to be taken in ascertaining your residential status so that you can correctly opt for eligibility to tax forms, rebates etc.
What is Income tax refund and How you can claim it?
Income tax refund is the excess tax paid by you which is refunded back by the Income Tax Department. For eg : tax you need to pay was Rs. 10,000 but you paid 15,000, then after filing your income tax return which would be showing tax refund of Rs. 5,000 the amount will be given back to you by the Income Tax Department.
You can now track the status of Income tax refund with our free tool Refund Status
What is and How to E-verify Income Tax Return?
A signed hard copy of ITR V can be sent to CPC Bangalore or it can be e verified online, to know more about steps to e-verify read this blog Click here
Is Income tax Act applicable only to residents?
No, Not only residents even the non residents are covered under the scope of Income tax Act. In other words, it applies to all persons who earn income in India irrespective of their residential status.
For whom is E-filing Mandatory?
Persons earning income of more than Rs. 5,00,000 in a year are compulsorily required to e-file their Income Tax Returns.
As per the New Forms issued by CBDT for Financial Year 2017-18
- Individuals and HUFs having income below Rs. 5 lakhs and Individual not have any income tax refund or
- Individual aged 80 years or above
Can file Paper ITR if they do not make any claim for refunds.
Can a return be filed after the due date? Fee u/s 234F!!
Yes, if you fail to file the return of income on or before the prescribed due date, then you can file a belated return. A belated return can be filed till the end of the relevant assessment year.
Example :-
Return for F.Y 2017-18 was say required to be filed latest till 31 July 2018. But, Mr Chopra fails to do so. Now, he can furnish belated return of income till 31st March 2019.
FEE u/s 234F
From the Financial Year 2017-18 onwards if you are submitting Belated Return then, Fee u/s 234F shall be levied as under
| Rs 5,000 | If you file after 31st July but till 31st December |
| Rs 10,000 | If you file after 31st December |
In case your total income does not exceed Rs 5 lakhs the fee shall be imposed upto Rs 1,000/- only.
How many years of income tax return can I file online in one go?
Voluntarily you can file only one year Income Tax Return now.
For e.g. : If you are filing return in July 2018, then you can only file ITR for
- Financial Year 2017-18 (being the relevant FY)
Can I claim deduction for my personal and household expenditure in calculating my income or profit?
No, you cannot claim any of such deductions or expenditures.
So far I have never paid any tax. If I file a return this year will the IT department ask me about my earlier years income?
The department does not always asks for your earlier year returns but it may ask you to file return of income for earlier years if it finds that you had taxable income in those years and you have not filed your income tax return despite being eligible for it.
Am I required to keep a proof of ITR filed? If yes then for how long?
Yes. Since legal proceedings under the income tax act can be initiated up to six years prior to the current financial year, you must maintain such documents at least for this period.
Finally, my income tax return has been filed, am I free now?
Yes, you are free now until you haven’t made any mistake while filing. A mistake can lead you to revise your return u/s 139 (5) or rectify u/s 154. We advise you to always take expert assistance before filing your income tax return to avoid such cases.
If you haven’t filed your return yet. What are you waiting for? File now! Just Click here!
Our guide on taxes has reached its end, and now you are ready to gain knowledge on the more complex topics. We know you are no more a tax beginner now, because you know it all, short and crisp! Kudos to you!!
In case of any doubts or queries, just comment below or Contact Us Now!
Income Tax Basics - Commonly used Abbreviations and their Full Forms
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
|---|---|
| AC | Assistant Commissioner |
| AG | Audit and General |
| AO | Assessing Officer |
| AY | Assessment Year |
| AS | Accounting Standards |
| CA | Current Asset |
| CG | Capital Gain |
| CL | Current Liability |
| Cr. | Credit |
| CP | Commercial Paper |
| DD | Demand Draft |
| Dr. | Debit |
| Dy. | Deputy |
| e- | Electronic |
| EC | Education Cess |
| FD | Fixed Deposit |
| FY | Financial Year |
| FS | Financial Statements |
| HC | High Court |
| HP | House Property |
| IB | Intelligence Bureau |
| IT | Income Tax |
| JC | Joint Commissioner |
| NI | Net Income |
| OD | Over Draft |
| O/S | Outstanding |
| PF | Provident Fund |
| P&L | Profit and Loss |
| PY | Previous Year |
| RD | Recurring Deposit |
| SC | Surcharge |
| u/s | Under section |
| WT | Wealth-tax |
| AAR | Authority of Advance Ruling |
| ADR | American Depository Receipt |
| AGI | Adjusted Gross Income |
| AIF | Alternative Investment Fund |
| AMC | Asset Management Company |
| AMT | Alternative Minimum Tax |
| AOPs | Association of Persons |
| AJP | Artificial Judicial Person |
| BOI | Body of Individuals |
| BSE | Bombay Stock Exchange |
| BSR Code | BASIC STATISTICAL RETURNS |
| C&AG | Comptroller and Auditor General of India |
| CFS | Consolidated Financial Statements |
| CFS | Cash Flow Statement |
| CII | Cost Inflation Index |
| CIT | Commissioner of Income Tax |
| CIT (A) | Commissioner of Income Tax (Appeal) |
| CIN | Corporate Identity Number |
| CIN | Challan Identification Number |
| COA | Cost of Acquisition |
| COI | Cost of Improvement |
| CPI | Consumer Price Index |
| CSR | Corporate Social Responsibility |
| CRR | Cash Reserve Ratio |
| CST | Central Sales Tax |
| DOB | Date of Birth |
| DTA | Deferred Tax Asset |
| DIN | Document Identification Number |
| DTL | Deferred Tax Liability |
| ECS | Electronic Credit System |
| EFT | Electronic Funds Transfer |
| ERI | e-Return Intermediary |
| EIN | Employer Identification Number |
| ESI | Employees' State Insurance |
| EVC | Electronic Verification Code |
| FBT | Fringe Benefit Tax |
| FII | Foreign Institutional Investor |
| FMV | Fair Market Value |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| GDR | Global Depository Receipt |
| Gov | Government |
| GST | Goods and Service Tax |
| GTI | Gross Total Income |
| HEC | Health and Educational Cess |
| HRA | House Rent Allowance |
| HUF | Hindu Undivided Family |
| Ind AS | Indian Accounting Standard |
| INR | Indian Rupee |
| IRR | Internal Rate of Return |
| ITA | Income Tax and Accounting |
| ITD | Income Tax Department |
| ITO | Income Tax Officer |
| ITR | Income Tax Return |
| KVP | Kisan Vikas Patra |
| LLC | Limited Liability Company |
| LLP | Limited Liability Partnership |
| LTC | Leave Travel Concession |
| LTU | Large Taxpayer Unit |
| LUT | Letter of Undertaking |
| Ltd | Limited |
| MAT | Minimum Alternate Tax |
| MIS | Management Information System |
| NAV | Net Asset Value |
| NOL | Net Operating Loss |
| NPS | National Pension System |
| NRE | (Non-Resident External) Account |
| NRI | Non-Resident Indian |
| NRO | Non-Resident Ordinary |
| NSC | National Saving Certificates |
| NSE | National Stock Exchange |
| OTP | One Time Password |
| PAN | Permanent Account Number |
| PIN | Personal Identification Number |
| Pvt | Private |
| PPF | Public Provident Fund |
| QIB | Qualified Institutional Buyer |
| RBI | Reserve Bank of India |
| RSE | Recognised Stock Exchange |
| SAT | Self Assessment Tax |
| SEZ | Special Economic Zone |
| STT | Security Transaction Tax |
| SIP | Systematic Investment Plan |
| SCN | Show Cause Notice |
| Sec | Section |
| SLR | Statutory liquidity ratio |
| TRP | Tax Return Preparer |
| TAN | Tax Deduction / collection account number |
| TCS | Tax Collected at Source |
| TDS | Tax Deduction at Source |
| TIN | Tax Payer’s Identification Number |
| TPO | Transfer Pricing Officer |
| VAT | Value Added Tax |
| VCC | Venture Capital Company |
| VCF | Venture Capital Fund |
| VCU | Venture Capital Undertaking |
| w.e.f | With effect from |
| ACES | Automation of Central Excise and Service Tax |
| ACIT | Assistant Commissioner of Income Tax |
| Asst. | Assistant |
| ASTO | Assistant Sales Tax Officer |
| CBDT | Central Board of Direct Tax |
| CBIC | Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs |
| CCIT | Chief Commissioner of Income Tax |
| CGST | Central Goods and Services Tax |
| CIT (A) | Commissioner of Income Tax (Appeal) |
| COGS | Cost of Goods Sold |
| CWIP | Capital Work-in-Progress |
| DCIT | Deputy Commissioner of Income Tax |
| DGIT | Director General of Income Tax |
| DGIT (E) | Director General of Income Tax (Exemption) DSIR |
| DTAA | Double Taxation of Avoidance Agreement |
| e- SMS | electronic Short Message Service |
| EFIN | Electronic Filing Identification Number |
| ELSS | Equity Linked Savings Scheme |
| ESOP | Employees Stock Option Plan |
| FIFO | First In First Out |
| GAAR | General Anti- Avoidance Rules |
| GAAP | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles |
| ICDS | Income Computation and Disclosure Standards notified by the Central Government under section 145(2) |
| IFRS | International Financial Reporting Standards |
| IFSC | Indian Financial System Code |
| IGST | Integrated Goods and Service Tax |
| IMPS | Immediate Payment Service |
| IRDA | Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India |
| ITAT | Income Tax Appellate Tribunal |
| ITIN | Individual Taxpayer Identification Number |
| JCIT | Joint Commissioner of Income Tax |
| LIFO | Last In First Out |
| LTCG | Long Term Capital Gains |
| MAGI | Modified Adjusted Gross Income |
| MCLR | Marginal Cost of funds based Lending Rate |
| MICR | Magnetic Ink Character Recognition |
| NEFT | National Electronic Funds Transfer |
| PATR | Patronage Dividend |
| PCIT | Principal Commissioner of Income Tax |
| RERA | Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 |
| REIT | Real Estate Investment Trust |
| RTGS | Real Time Gross Settlement |
| PGBP | Profits and Gains of Business or Profession |
| SCSS | Senior Citizens Saving Scheme, 2004 |
| SEBI | Security and Exchange Board of India |
| SGST | State Goods and Services Tax |
| SHEC | Secondary and higher educational cess |
| STAT | Sales Tax Appellate Tribunal |
| STCG | Short Term Capital Gains |
| ULIP | Unit Linked Insurance Plan |
| UTGST | Union Territory Goods and Service Tax |
| CC-ITA | Chief Council - Income Tax and Accounting |
| CENVAT | Central Value Added Tax |
| e- SMS | electronic Short Message Service |
| EFTPS | Electronic Federal Tax Payment System |
| FATCA | Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act |
| IT RATE | Income-tax rate |
| IT+HEC | Income Tax plus Health and Educational Cess |
| IT+SC | Income Tax plus surcharge on income –tax |
| IT+SC+EC | Income Tax plus surcharge on income –tax plus education cess on income-tax and surcharge |
| IT+SC+EC+SHEC | Income Tax plus surcharge on income –tax plus education cess plus secondary and higher education cess on income –tax and surcharge |
| IT+SC+HEC | Income Tax plus surcharge on income –tax plus health and education cess on income-tax and surcharge |
| KVATIS | Kerala Value Added Tax Information System |
| MACRS | Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System |
| TINXSYS | Tax Information Exchange System |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q- What is the administrative framework of Income-tax?
Ans. Central board of direct taxes administers the direct tax law through income tax department. Therefore income tax department is administers the income tax law under the supervision of CBDT.
Q- What is the period for which a person’s income is taken into account for the purpose of Income-tax?
Ans. income tax is charged on the annual income of assessee therefore period of 1st April to 31st March is taken as income period.
Q- From where can I take the help of any expert on Income-tax related matters?
Ans. For income tax related matters expert can hire on tax 2 win website, where you can find answers to all your queries.
Q- In the Challan there are terms like Income-tax on companies & Income-tax other than companies. What do they mean?
Ans. These terms are in reference of tax applicability. taxes paid by companies are corporate tax and for that challan contains the details of income tax on companies and for the others income tax other than companies.
Q- How is advance tax calculated and paid?
Ans. Advance tax is paid by the assessee having tax liability in excess of rupees 10000. it is calculated on the current income and paid in 4 installments.
Q- What is tax on regular assessment and how is it paid?
Ans. Tax on regular assessment is the tax paid by the taxpayer on notice of demand. notice of demand means an additional tax is paid by assessee.
Q- What are the precautions that I should take while filling-up the tax payment challan?
Ans. PAN and correct name and address on challan is quote correctly and indicate FY and AY while filling the challan, separate challan shall be used for each payment and correct code is selected.
Q- How can I know that the Government has received the amount deposited by me as taxes in the bank?
Ans. Details of tax deposited by the assessee is shown in 26AS as self assessment tax. assessee can check this on 26 AS. NSDL also provides the service of challan status enquiry, assessee can take the information from NSDL website.
Q- What should I do if my tax payment particulars are not found against my name on the website?
Ans. There may be various possible reasons that amount is not shown in 26AS like PAN not correctley quoted, Incorrect PAN quoted etc. by rectifying the reasons details will be shown on website.
Q- Is my responsibility under the Income-tax Act over once taxes are paid?
Ans. No, you are now responsible for ensuring that taxes paid are shown in the tax credit statement. and if taxes are not credit in statement possible rectification shall be made.
Q- What is tax on regular assessment and how is it paid?
Ans. Tax on regular assessment is the tax paid by the taxpayer on notice of demand. notice of demand means an additional tax is paid by assessee.
Q- Who is an Assessing Officer?
Ans. Assessing officer ia officer of income tax department and AO is given jurisdiction over an area.
Q- Income-tax is levied on the income of every person. As per Income-tax Law what constitutes income?
Ans. Income is defined under the 5 heads of income. that are salary, house property, business and profession, capital gains, and other sources. income constitutes under these heads are covered under the income.
Q- What is exempt income and taxable income?
Ans. Incomes which are not chargeable to tax is exempt income and the income which are chargeable to tax are taxable income.
Q- What is revenue receipt and capital receipt?
Ans. Revenue receipts are in the nature of revenue like business income, salary income etc. and Capital receipts are those which are not in the nature of revenue like sale of building, gold etc.
Q- Are all receipts, i.e., capital and revenue receipts, charged to tax?
Ans. All the revenue receipts are taxable unless exemptions are provided in law, and capital receipts are exempt from taxes unless there is specific provisions for taxing them.
People also ask
- Types Of Income, Deductions, Tax Slabs & e-Filing ITR Online
- Advance Tax: Calculate & Make Payment Online
- URN Status - How to check your URN Status?
- Udyog Aadhar Registration
- Self Assessment Tax
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
- Section 92E - Furnishing Reports For International Transactions
- Presumptive Income Taxation Under Income Tax Act
- Section 44ADA - Presumptive Taxation
- Section 44AD - Presumptive Taxation
- Section 12A - Tax Exemptions for Charitable Trusts & NGOs
- PRAN Card - Permanent Retirement Account Number Guide
- Minimum Alternative Tax - Applicability & Calculation of MAT Credit
- Section 56 - Taxation of Wedding/Marriage Gifts Received
- Income Tax on Dividends - How dividends are taxed?
- Income Tax on Awards & Prizes - Lottery, Game Shows, Puzzle
- Claim Tax Credit on Foreign Income of a Resident Indian
- Income Tax Audit Under Section 44AB of Income Tax Act
- Income Tax Act & Laws - 1961 & 1962
- Gross Total Income - Computation of Total Taxable Income
- Form 10E - Claim Income Tax Relief under Section 89(1)
- Dividend Mutual Funds
- Cost Inflation Index (CII)
- Agricultural Income - Types & Tax Calculation
- 5-Year Post Office Recurring Deposit
- Voter ID /Election Card - Documents, Application, Eligibility
- Total Income - How to Calculate It?
- Income Tax India E - filing Login
- KYC (Know Your Customer) - How to Check Your KYC Status
- Section 87A - Tax Rebate under Section 87A
- Union Budget 2019 - Key Highlights
- Income Tax Form 60
- Income Tax For Self Employed Business, Profession & Freelancers
- Govt. Jobs v/s Private Jobs - Comparative study on benefits
- Section 234F - Penalty for Late Filing of Income Tax Return
- Section 234C - Interest on Deferred Payment of Advance Tax
- Section 234B - Interest on Delayed Payment of Advance Tax
- Section 234A - Interest Penalty on Delayed ITR Filing
- Section 234F - Penalty for Late Filing of Income Tax Return

